Suzanne D Colson 1, Judith H Meek, Jane M Hawdon
Abstract
Background: Despite widespread skills-teaching, 37% of UK mothers initiating breastfeeding stop by six weeks suggesting a need to reappraise current support strategies. Rooting, sucking and swallowing have been studied extensively but little is known about the role other primitive neonatal reflexes (PNRs) might play to support breastfeeding.
Aims: To describe and compare PNRs observed during feeding, investigating whether certain feeding behaviours and positions, collectively termed Biological Nurturing, (BN) are associated with the release of those reflexes pivotal in establishing successful feeding.
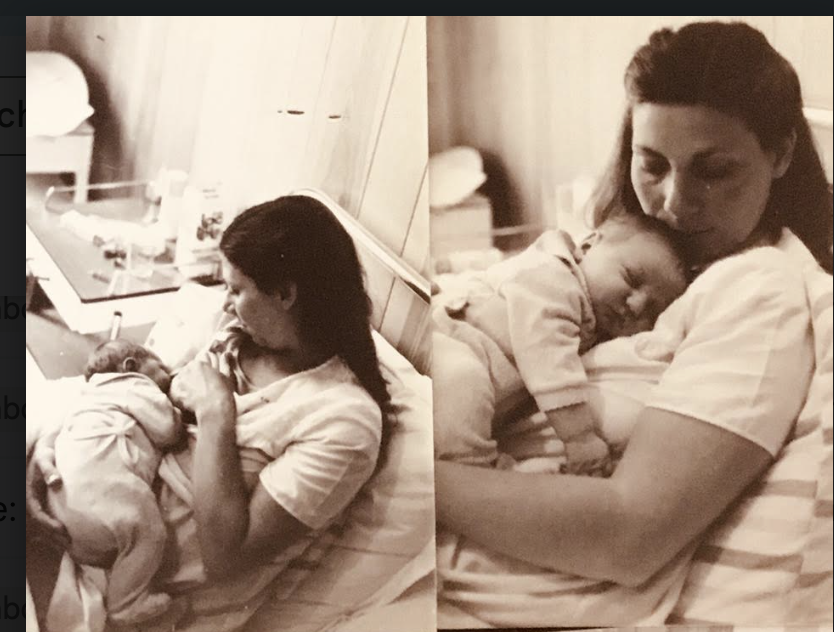
Method: 40 breastfed healthy term mother/baby pairs were recruited using quota sampling to stratify term gestational age. Feeding sessions were videotaped in the first postnatal month, either in hospital or at home.
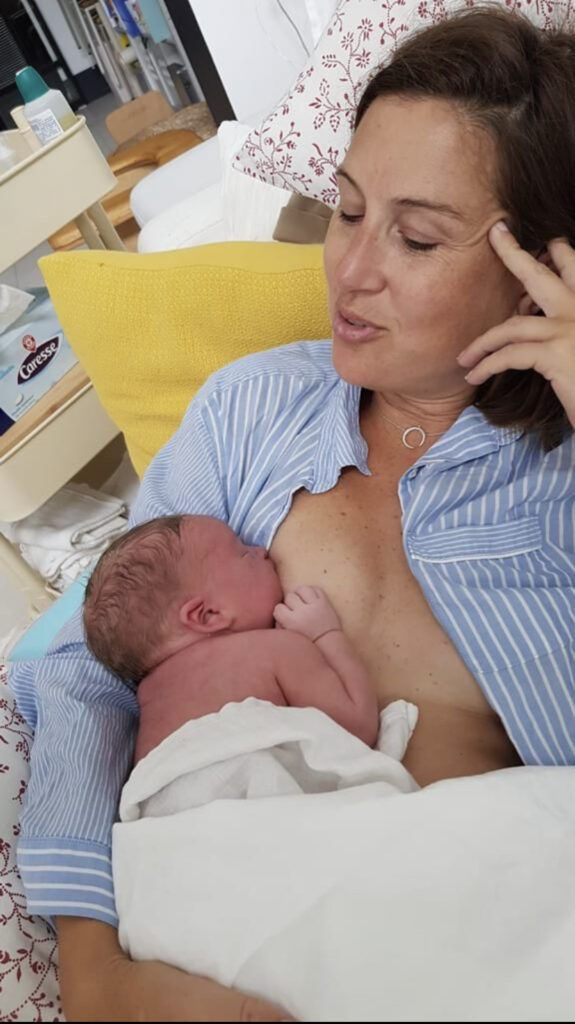
Findings: 20 PNRs were validated and classified into 4 types (endogenous, motor, rhythmic and anti-gravity) and 2 functional clusters (finding/latching, milk transfer) either stimulating or hindering feeding. Significantly more PNRs were observed as stimulants in semi-reclined postures (BN) than when mothers were upright or side-lying (p=<0.0005).
Discussion: This study is the first to describe a range of semi-reclined maternal postures interacting with neonatal positions, releasing maternal instinctual behaviours and PNRs stimulating breastfeeding. Traditionally the human neonate has been considered a dorsal feeder with pressure needed along the baby’s back. Compelling visual data here illustrate that the newborn is an abdominal feeder and, like some other animals, displays anti-gravity reflexes aiding latch. Findings suggest that breastfeeding initiation is innate for both mother and baby, not learned, thus challenging the routine skills-teaching currently central to breastfeeding support.